Using AI in Engineering, 80 Years of FEA, Open Source Aeroacoustics
📈 An investment in knowledge pays the best interest.
💻 The Evolution in Physics Modeling & When to Use AI! - Andy Fine
🤓 Eighty Years of the Finite Element Method: Birth, Evolution, and Future
This document presents comprehensive historical accounts on the developments of fnite element methods (FEM) since 1941, with a specifc emphasis on developments related to solid mechanics. We present a historical overview beginning with the theoretical formulations and origins of the FEM, while discussing important developments that have enabled the FEM to become the numerical method of choice for so many problems rooted in solid mechanics.
💻 Higher crash safety of composites through simulation with LS-DYNA
Crashworthiness is one of the most critical factors that every car manufacturer must take into account during the development phase of a vehicle. The safety of occupants and pedestrians depends largely on the vehicle's crashworthiness. An optimal vehicle body design for crash performance ensures that occupants and pedestrians are maximally protected in traffic accidents.
At the same time, regulations for vehicle crashworthiness are becoming increasingly stringent. To reliably and efficiently predict and demonstrate the crashworthiness of lightweight composite components, particular expertise is required to simulate highly dynamic processes and understand the composite materials used.
💧Understand the Physics of Re-Entry Vehicles Using Numerical Modeling and Simulation
Recreating the atmospheric conditions of Mars is a challenging task. Traditional continuum mechanics assumptions are ineffective at high Mach numbers and low densities, making it difficult to replicate re-entry velocity and temperature in wind tunnels. In such situations, numerical methods and computer simulations help understand the underlying physics of re-entry vehicles.
In this detailed case study, learn about computation methodology, atmospheric chemistry modelling, and test cases for vehicle re-entry into the Mars atmosphere.
🎬 Channel of the Week - Navasto
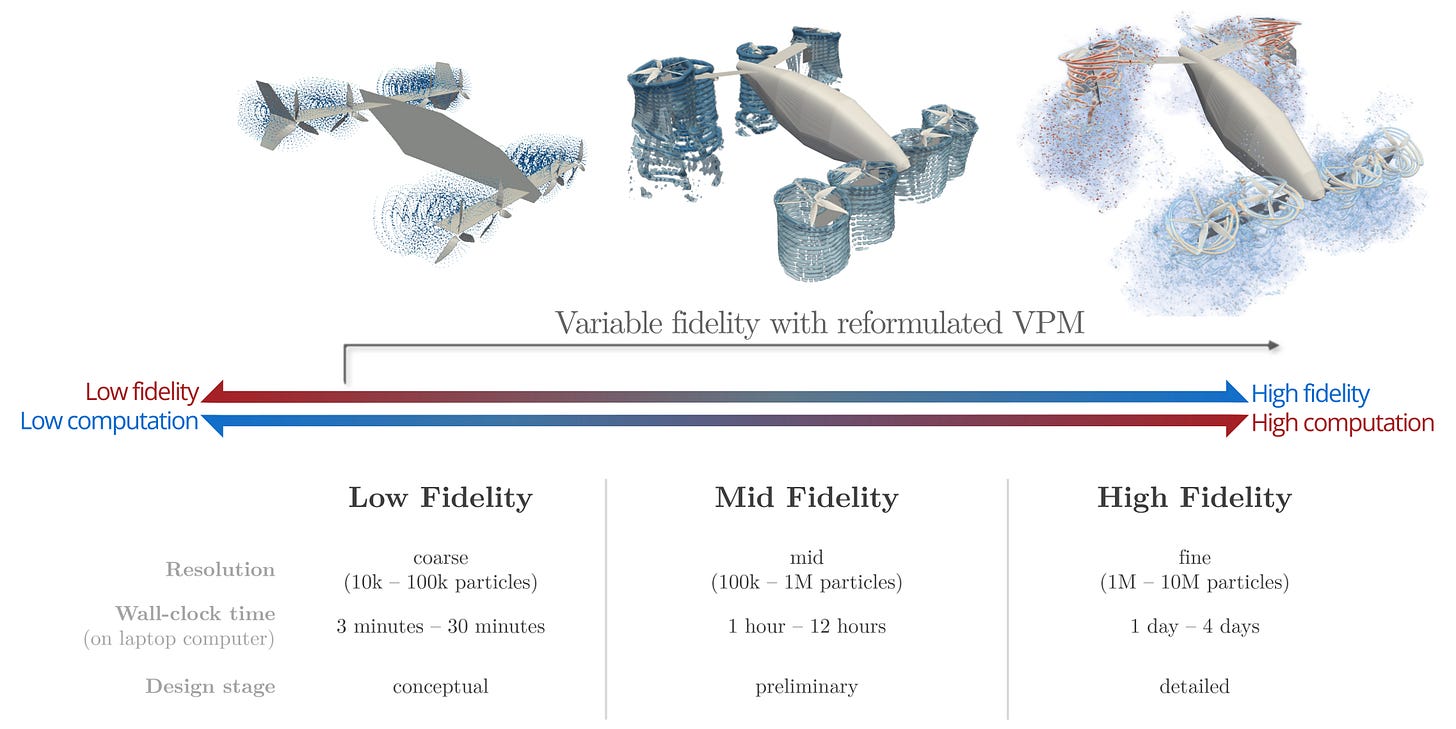
💻 Engineering Tool of the Week - FLOWUnsteady
FLOWUnsteady is an open-source variable-fidelity framework for unsteady aerodynamics and aeroacoustics based on the reformulated vortex particle method (rVPM). This suite brings together various tools developed by the FLOW Lab at Brigham Young University: Vortex lattice method, strip theory, blade elements, 3D panel method, and rVPM. The suite also integrates an FW-H solver and a BPM code for tonal and broadband prediction of aeroacoustic noise. In the low end of fidelity, simulations are similar to a free-wake method, while in the high end simulations become meshless large eddy simulations.
📚Book of the Week
Data-Driven Science and Engineering - Machine Learning, Dynamical Systems, and Control
Data driven discovery is revolutionizing how we model, predict. control complex systems. Now with Python and MATLAB®, this textbook trains mathematical scientists and engineers for the next generation of scientific discovery by offering a broad overview of the growing intersection of data driven methods, machine learning, applied optimization.
Topics range from introductory to research level material, making it accessible to advanced undergraduate and beginning graduate students from the engineering and physical sciences. The second edition features new chapters on reinforcement learning and physics informed machine learning, significant new sections throughout. chapter exercises.
❤️ Support the Blog & Newsletter
Let’s connect on Twitter, Instagram or LinkedIn!
For any business-related issues or collaborations, email me at support@jousefmurad.com!
Keep engineering your mind! 🧠
Jousef